Originally posted on April 16, 2024 @ 10:45 pm
SOUNDPROOFING
Effective soundproofing with suspended ceilings is crucial for creating environments that are conducive, productive, concentration, and comfort.
Suspended ceilings provide a versatile platform for implementing these solutions that can significantly reduce airborne and impact noise transmission within a space.
In residential settings for instance, it can improve privacy by minimizing noise between rooms or floors, allowing individuals to enjoy peace and quietness within their homes.
And in commercial spaces, such as offices, studios, or entertainment venues, soundproofing is essential for creating conducive environments for work, recording, or performances without disturbances from external sources.
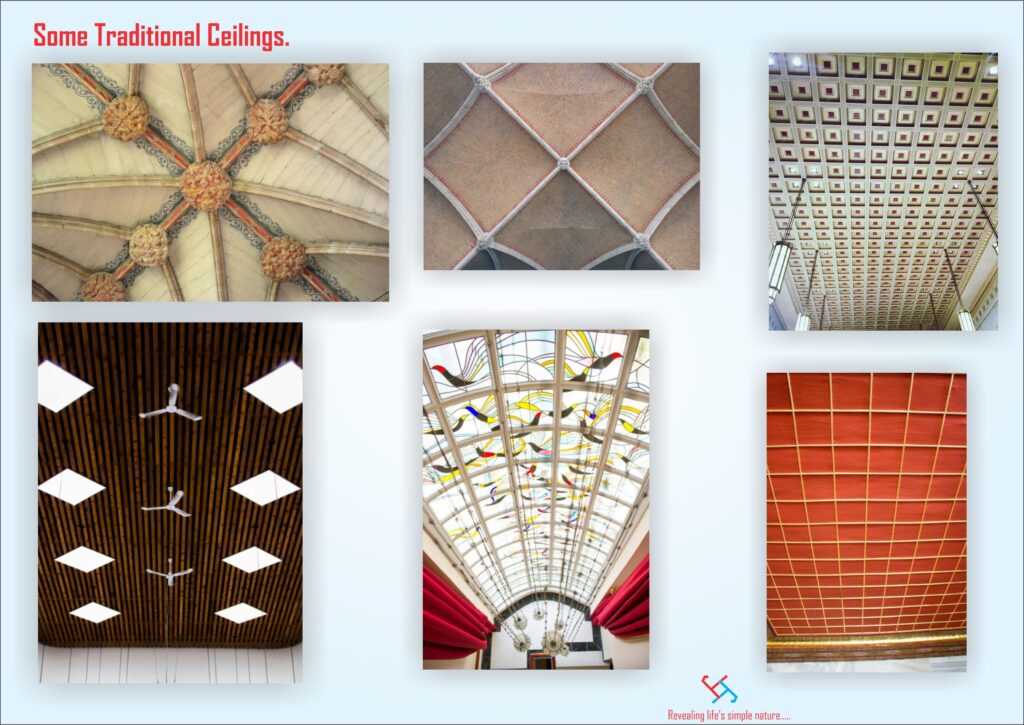
HISTORY OF SOUNDPROOFING WITHOUT SUSPENDED CEILINGS SOLUTION
The history of soundproofing dates back to Ancient times when the techniques to mitigate noise and control sound were thick walls/stones, heavy curtains, dense materials (mud bricks), vaulted ceilings and amphitheater designs.
The introduction of sound-absorbing materials such as fiberglass insulation, acoustic panels, and foam baffles revolutionized the field of soundproofing, enabling architects, engineers, and designers to create environments with precise control over sound quality and acoustics.
Today, soundproofing continues to evolve with advancements in materials science, digital technology, and architectural design.
Therefore, the history of soundproofing without the formal study of acoustics solutions demonstrates humanity’s ongoing quest to create quieter, more comfortable, productive and acoustically optimized environments.
But before we unveil how suspended ceiling takes the front row by blocking out external noise from entering a space or preventing sound from escaping into adjacent spaces, let’s first understand some self-discovering principles of productive soundproofing.
3 PRINCIPLES OF SOUNDPROOFING
- How does sound travels and interact with different materials
AIR – Sound absorption in air occurs when sound waves encounter surfaces or objects that absorb or scatter the energy, reducing the intensity of the sound.
SOLID – Solids are denser and allowing sound waves to travel faster and with less attenuation.
POROUS MATERIAL – This absorption mechanism reduces the reflection and transmission of sound waves, making porous materials effective for soundproofing.
- How do you identify the source of the noise
EXTERNAL NOISE – It originates from traffic, aircraft, construction activities, industrial machinery, and environmental factors such as wind and rain
INTERNAL NOISE – Talking, music, footsteps, plumbing, electrical equipment, or appliances are avenues of creating internal noise
IMPACT NOISE – Usually caused by physical impact or vibrations, such as footsteps, dropping objects, or mechanical equipment
AIRBORNE NOISE – It include speech, music, television, appliances, and outdoor activities
- How do you select appropriate soundproofing materials and techniques?
- Check for any source of noise; the frequency, intensity, and duration of the noise will help determine the most effective soundproofing strategies.
- Assess the Space; the type of surfaces the presence of openings and the activities taking place in the space will give a clue.
- Familiarize with the principles of soundproofing that are absorption, blocking, and isolation.
- Explore the wide range of soundproofing materials available on the market.
- Consult with Experts if necessary; they can offer tailored recommendations
Whether you desire to create a peaceful home, office, and event halls, worship centers, recording studio, or minimize noise even in a commercial space, soundproofing offers effective solutions with Suspended Ceiling Systems.
SOUNDPROOFING TECHNIQUES
Soundproofing techniques whose aim is to create quieter and more comfortable environments. Here are 7 techniques that appropriately will boost sound production in any allotted space or environment
- Sealing and Insulation: Sealing helps to prevent sound leakage while Insulation are materials (fiberglass, mineral wool, or acoustic foam) that fills cavities and dampen sound vibrations.
- Mass-Loaded Vinyl: MLV is a versatile soundproofing material that ensure an effective blockage of airborne sound transmissions
- Decoupling: It separates structural elements and minimize sound transmission through physical contact. Resilient channels, acoustic hangers, or isolation pads are instrumental in creating the separation between surfaces, reducing the transfer of vibrations and impact noise.
- Double Glazing: To reduce noise infiltration from outside sources, there is need to upgrade to double or triple-pane windows with laminated or acoustic glass .
- Acoustic Windows: The secondary window panels or plugs develop further barrier against sound transmission
- Strategic Room Design: If minimizing sound reflections and reverberations is your goal, you should optimize the layout and design of your space such as the placement of furniture and decorations to absorb or distribute sound waves effectively.
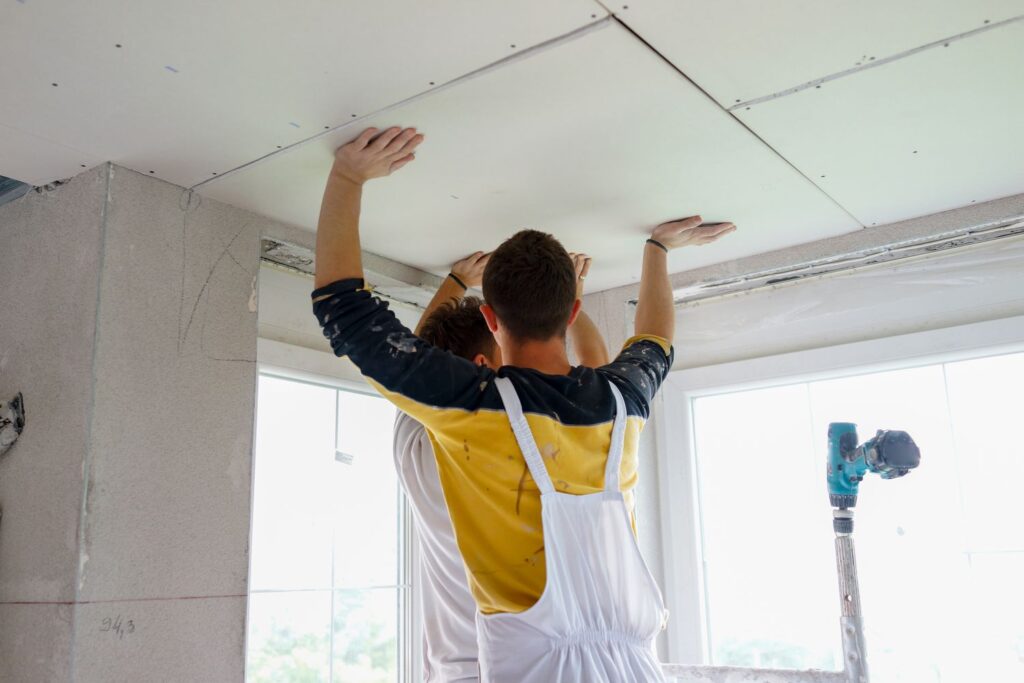
- Suspended Ceiling: Create space between the original ceiling and the suspended ceiling tiles, allowing for the installation of sound-absorbing materials such as acoustic panels that absorb airborne sound waves and reduce reverberation within the space, effectively improving acoustics and minimizing noise transmission.
WHY SUSPENDED CEILING LEAD OTHERS
As earlier said that soundproofing aims at the reduction or controlling of the transmission of sound waves between floors or rooms using suspended ceiling solutions.
Suspended ceiling is best preferred beacuse of its power of integration with other soundproofing techniques.
Furthermore, suspended ceilings offer the flexibility to integrate additional soundproofing techniques
REASONS FOR ITS UNIQUE QUALITIES
- Suspended ceilings provide an excellent opportunity to incorporate sound-absorbing insulation materials such as fiberglass, mineral wool, or acoustic foam.
These materials can be installed above the suspended ceiling tiles to absorb airborne sound and reduce reverberation within the space.
- The installation of resilient channels, rubber isolators, or spring-loaded hangers between the ceiling suspension grid and the building framework reduce the transfer of vibrations and impact noise.
- Mass-loaded vinyl (MLV) barriers can be installed above the suspended ceiling to add mass and density, enhancing the soundproofing performance. MLV sheets can be laid on top of the ceiling grid
- Suspended ceiling systems offer the flexibility to incorporate specialized acoustic window panels and tiles with enhanced sound-absorbing functionalities
- With suspended ceiling systems, acoustic sealants can be applied to seal gaps, block sound transmission between ceiling tiles and the surrounding structure.
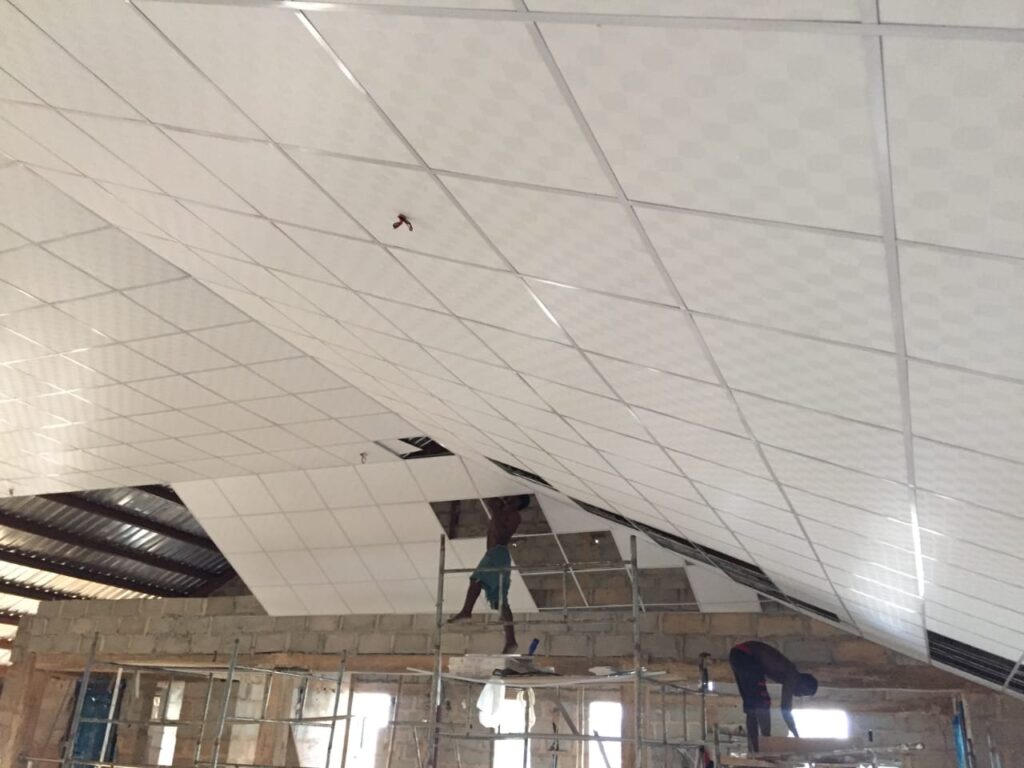
TYPES OF SUSPENDED CEILINGS
Here are the different types of suspended ceiling systems.
- Traditional drop ceilings
- Acoustic ceiling tiles
- Custom-designed options
4 COMMONLY USED MATERIALS FOR MANUFACTURING SUSPENDED CEILING
- Mineral wool – It is non-combustible with excellent fire resistance properties, making it a safe and durable choice.

Mineral wool is also resistant to moisture, mold, pests thereby it is suitable for installation in humid or damp environments
2. Fiberglass – They are lightweight, durable, and easy to handle, making them suitable for installation in a wide range of environments.

3. Perforated metal panels – It is durable, fire-resistant, and easy to clean. It is made from thin sheets of metal (aluminum or steel) that have been perforated with small holes or patterns.
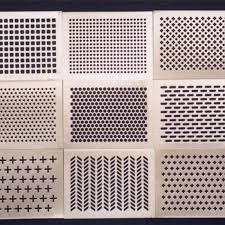
4. Sound-absorbing fabrics – They are lightweight, flexible, and easy to install, making them suitable for a variety of ceiling designs and configurations. Sound-absorbing fabrics also come in a wide range of colors, textures, and patterns









